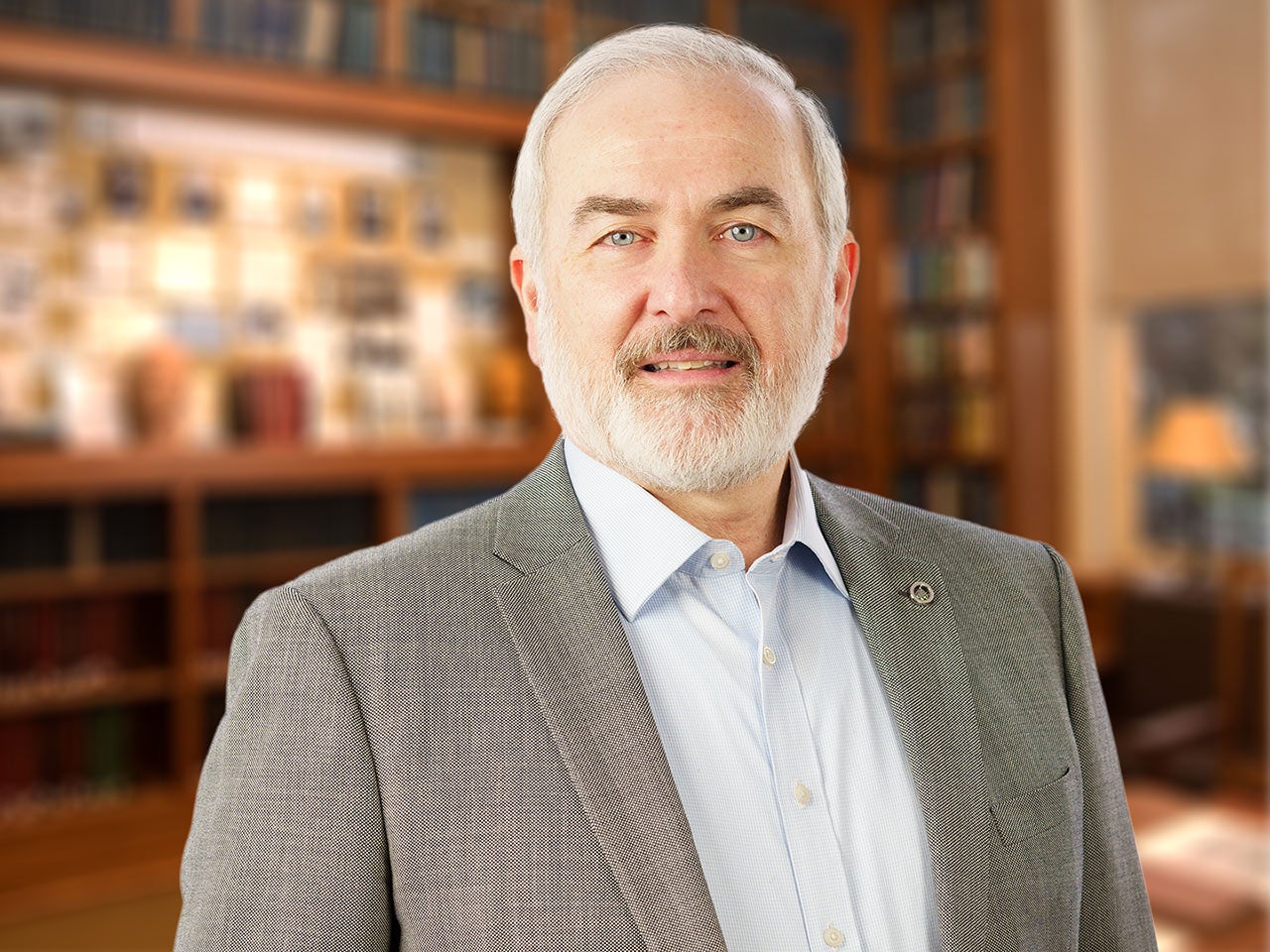
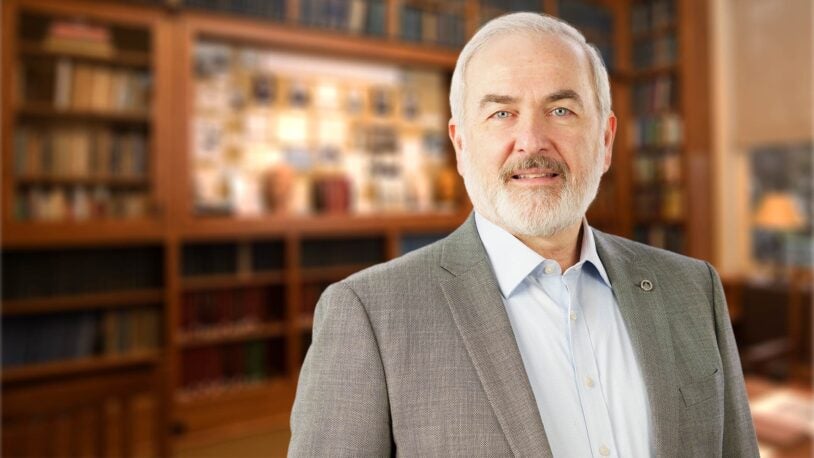
Adrian R. Krainer
Professor
St. Giles Foundation Professor
Cancer Center Program Co-Leader
Ph.D., Harvard University, 1986
krainer@cshl.edu | 516-367-8417
Our DNA carries the instructions to manufacture all the proteins needed by a cell. After each gene is copied from DNA into RNA, the RNA message is "spliced" - an editing process involving precise cutting and pasting. I am interested in how splicing normally works, how it is altered in genetic diseases and cancer, and how we can correct these defects for therapy.
Adrian Krainer’s lab studies the mechanisms of RNA splicing, ways in which they go awry in cancer and genetic diseases, and the means by which faulty splicing can be corrected. For example, they have studied splicing in spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a neuromuscular disease that is the leading genetic cause of death in infants. In SMA, a gene called SMN2 is spliced incorrectly, making it only partially functional. The Krainer lab found a way to correct this defect using a powerful therapeutic approach. It is possible to stimulate SMN protein production by altering mRNA splicing through the introduction into cells of chemically modified pieces of RNA called antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs). Following extensive work with ASOs in mouse models of SMA, one such molecule, known as nusinersen or Spinraza, was taken to the clinic, and at the end of 2016 it became the first FDA-approved drug to treat SMA, by injection into the fluid surrounding the spinal cord. The Krainer lab is currently using antisense technology to develop therapies for other diseases caused by splicing defects, including familial dysautonomia, and to target a cancer-specific alternative-splicing event that controls the Warburg effect. In addition, they are applying antisense technology downregulate activated oncogenes, e.g., a mutant oncohistone that causes diffuse midline glioma, a lethal pediatric brain cancer. The Krainer lab has also worked to shed light on how splicing factors and alternative splicing promote cancer progression in the context of breast, liver, brain, pancreatic, and blood malignancies. Finally, the lab continues to study fundamental mechanisms of splicing and its regulation, focusing on the precise recognition of highly diverse intronic and exonic pre-mRNA features by various spliceosome components.
2024 The Albany Prize in Medicine & Biomedical Research
2022 August M. Watanabe Prize in Translational Research, Indiana University School of Medicine
2021 Jacob & Louise Gabbay Award in Biotechnology and Medicine, Brandeis University
2021 Wolf Prize in Medicine from the state of Israel
2020 Takeda Pharmaceuticals & NY Academy of Sciences Innovators in Science Senior Scientist Award in Rare Diseases
2020 Ross Prize in Molecular Medicine, Feinstein Institute
2020 Gregor Johann Mendel Medal for Outstanding Achievements in Science, Brno, Czech Republic
2020 Member, National Academy of Sciences
2019 Member, National Academy of Medicine
2019 Adrian Krainer wins 2019 Peter Speiser Award
2019 Life Sciences Breakthrough Prize
2019 Doctorate Honoris Causa, Tel Aviv University
2019 International Prize for Translational Neuroscience, Gertrud Reemtsma Foundation and Max Planck Society
2019 RNA Society Lifetime Achievement Award
2019 Bermuda Principles Award
2019 Peter Speiser Award in Pharmaceutical Sciences, ETH Zurich
2018 National Academy of Inventors Fellow, Adrian Krainer
2018 Breakthrough Prize to CSHL professor for SMA research
2017 Inventor of the Year, New York Intellectual Property Law Association
2016 Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
2012 National Institutes of Health MERIT Award
President’s essay: We are science, and science is crucial
June 2, 2025
With public research funding under threat in the U.S., CSHL President Bruce Stillman outlines the stakes for people in our communities and abroad.
2024 Double Helix Medal recipient Dr. Katalin Karikó
December 10, 2024
She created the blueprint for mRNA vaccines. This year, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory recognized her groundbreaking research and pioneering spirit.
Adrian Krainer wins Albany Prize for biomedical research
October 8, 2024
A pioneer in the burgeoning field of RNA therapeutics, Krainer has now received America’s second-highest prize in medicine.
RNA splicing’s spotters
June 10, 2024
RNA therapeutics pioneer CSHL Professor Adrian Krainer has discovered a link between two important regulator proteins, SRSF1 and DDX23.
President’s essay: The continuous cycle of discovery
May 30, 2024
CSHL President & CEO Bruce Stillman discusses our institution’s societal impacts and global connections as forces for further scientific progress.
Why some RNA drugs work better than others
March 6, 2024
CSHL’s Justin Kinney and Spinraza inventor Adrian Krainer tested the newly approved SMA treatment, risdiplam, and another RNA therapeutic, branaplam.
Laying the groundwork for drug discoveries
August 8, 2023
A new partnership between CSHL and one of the world’s leading biotech investors could streamline this process and help change society for the better.
Eight serving one: CSHL volleyball mid-season report
August 2, 2023
CSHL’s 32nd Volleyball League season sees eight teams battling for the coveted Tiernan Cup and a year’s worth of bragging rights.
Adrian Krainer awarded honorary IADR membership
June 21, 2023
Krainer was recognized for his pioneering research on spinal muscular atrophy and RNA therapeutics.
President’s essay: Bringing bold visions to life
May 26, 2023
CSHL President & CEO Bruce Stillman sees the Laboratory as a global hub for scientific expertise and a powerful launchpad for early-career scientists.
Selected Publications
SRSF1 interactome determined by proximity labeling reveals direct interaction with spliceosomal RNA helicase DDX23
21 May 2024 | Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | 121(21):e2322974121
Segovia, Danilo; Adams, Dexter; Hoffman, Nickolas; Safaric Tepes, Polona; Wee, Tse-Luen; Cifani, Paolo; Joshua-Tor, Leemor; Krainer, Adrian;
Specificity, synergy, and mechanisms of splice-modifying drugs
29 Feb 2024 | Nature Communications | 15(1):1880
Ishigami, Yuma; Wong, Mandy; Martí-Gómez, Carlos; Ayaz, Andalus; Kooshkbaghi, Mahdi; Hanson, Sonya; McCandlish, David; Krainer, Adrian; Kinney, Justin;
Splicing Factor SRSF1 Promotes Pancreatitis and KRASG12D-Mediated Pancreatic Cancer
7 Jul 2023 | Cancer Discovery | 13(7):1678-1695
Wan, Ledong; Lin, Kuan-Ting; Rahman, Mohammad; Ishigami, Yuma; Wang, Zhikai; Jensen, Mads; Wilkinson, John; Park, Youngkyu; Tuveson, David; Krainer, Adrian;
Antisense oligonucleotide therapy for H3.3K27M diffuse midline glioma
12 Apr 2023 | Science Translational Medicine | 15(691):eadd8280
Zhang, Qian; Yang, Lucia; Liu, Ying; Wilkinson, John; Krainer, Adrian;
Counteracting chromatin effects of a splicing-correcting antisense oligonucleotide improves its therapeutic efficacy in spinal muscular atrophy
9 Jun 2022 | Cell | 185(12):2057-2070.e15
Marasco, Luciano; Dujardin, Gwendal; Sousa-Luís, Rui; Liu, Ying; Stigliano, Jose; Nomakuchi, Tomoki; Proudfoot, Nick; Krainer, Adrian; Kornblihtt, Alberto;
All Publications
Intra-amniotic antisense oligonucleotide treatment improves phenotypes in preclinical models of spinal muscular atrophy
14 May 2025 | Science Translational Medicine | 17(798):eadv4656
Borges, Beltran; Brown, Stephen; Chen, Wan-Jin; Clarke, Maria; Herzeg, Akos; Park, Jae; Ross, Joshua; Kong, Lingling; Denton, Madeline; Smith, Amy; Lum, Tony; Zada, Fareha; Cordero, Marco; Gupta, Nalin; Cook, Sarah; Murray, Heather; Matson, John; Klein, Stephanie; Bennett, C; Krainer, Adrian; MacKenzie, Tippi; Sumner, Charlotte;
Microbial metabolite ammonia disrupts TGF-β signaling to promote colon cancer.
29 Apr 2025 | Journal of Biological Chemistry | 301(6):108559
Bhowmick, Krishanu; Yang, Xiaochun; Mohammad, Taj; Xiang, Xiyan; Molmenti, Christine; Mishra, Bibhuti; Dasarathy, Srinivasan; Krainer, Adrian; Hassan, Md; Crandall, Keith; Mishra, Lopa;
New insights into biomarkers and risk stratification to predict hepatocellular cancer
23 Apr 2025 | Molecular Medicine | 31(1):152
Li, Katrina; Mathew, Brandon; Saldanha, Ethan; Ghosh, Puja; Krainer, Adrian; Dasarathy, Srinivasan; Huang, Hai; Xiang, Xiyan; Mishra, Lopa;
Splice-switching ASOs targeting an Alu-derived exon in the AURKA 5'UTR collapse an SRSF1-AURKA-MYC oncogenic circuit in pancreatic cancer
15 Apr 2025 | bioRxiv
Kral, Alexander; Jia, Lu; Sim, GeunYoung; Wan, Ledong; Krainer, Adrian;
PKM splice-switching ASOs induce upregulation of dual-specificity phosphatases and dephosphorylation of ERK1/2 in hepatocellular carcinoma
22 Feb 2025 | Journal of Biological Chemistry | :108345
Voss, Dillon; Kral, Alexander; Sim, GeunYoung; Utama, Raditya; Lin, Kuan-Ting; Cizmeciyan, Chris; Schafer, Balazs; Cunniff, Patrick; Vakoc, Christopher; Caruthers, Marvin; Mishra, Lopa; Krainer, Adrian;