Autism
What is Autism?
Autism and autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) represent a group of developmental disorders ranging from autistic disorder, which is severe, to the milder Asperger syndrome. ASDs are characterized by impaired social interactions, problems with verbal and nonverbal communication, repetitive behaviors, and severely limited activities and interests. ASDs are understood to affect an estimated 1 in 68 children (as reported by the CDC). The risk is three to four times higher in males than females.
CSHL researchers are applying leading-edge scientific expertise in genetics, genomics and neuroscience to understand the causes of ASDs.
Genetics and genomics researchers scan and analyze genomes in an effort to understand the complex genetics of autism. Breakthrough discoveries made at CSHL about variations in human genome structure have been especially revealing. CSHL’s pathbreaking work has demonstrated the importance in autism of spontaneous gene copy-number variations (CNVs)—mutations that appear in an autistic child but not in the genome of that child’s mother or father.
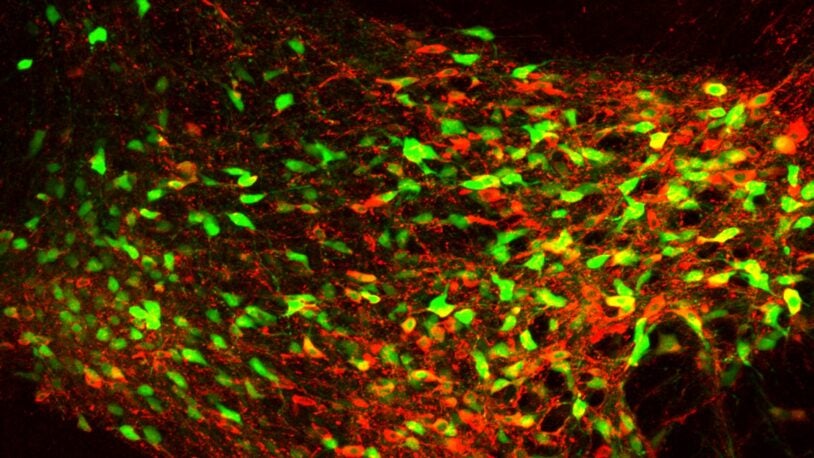
To better study autism, CSHL scientists have engineered a mouse model that replicates in a living mouse one serious genetic mutation frequently found in children with autism. These mice display many behaviors associated with ASDs and are an invaluable resource for future diagnostics and treatments.
CSHL experts in computational biology use advanced statistical analysis to examine the incidence of autism in families. This analysis is the basis for a new “unified theory” of autism’s genetic basis. The theory developed at CSHL helps to account for the observation that males are more likely to be affected by ASDs than females.
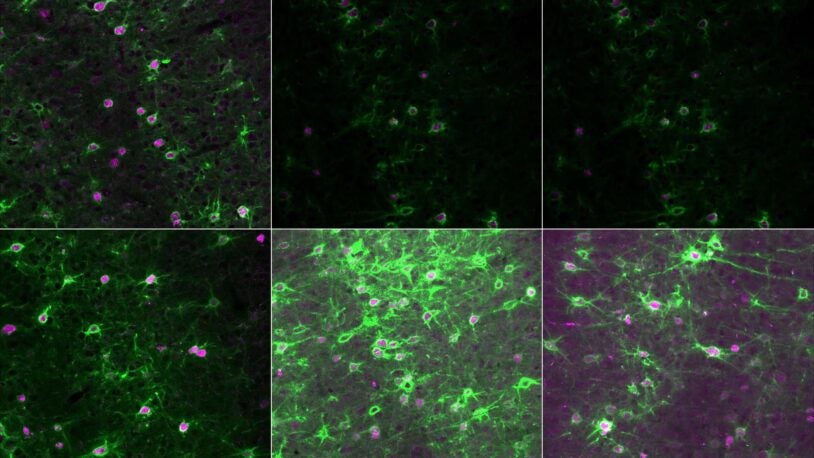
CSHL neuroscientists study the development, structure and function of neural circuits in the brain. Problems in circuitry are involved in most neuropsychiatric illnesses and we are looking for what specifically goes awry in the autistic brain.
- New study casts sharpest light yet on genetic mysteries of autism
- Autism genetically linked to Fragile-X Syndrome
- Autism mouse model developed
- Role of spontaneous mutations in ASDs
- “Unified Theory” of Autism
- Autism and hearing
- Sensory integration and decision-making
- Lucas Cheadle, Ph.D.
- Alea Mills, Ph.D.
- Stephen Shea, Ph.D.
- Michael Wigler, Ph.D.
- Anthony Zador, M.D., Ph.D.
At the Lab Episode 3: Autism Awareness Month
April 16, 2024
It’s Autism Awareness Month! CSHL Professor Ivan Iossofiv shares what researchers know about autism so far and how they plan to uncover its origins.
Animal behavior quiz
December 20, 2023
Take this short quiz to see how much you know about the science of social behavior.
Reactivate, repurpose, and rewire the brain
October 4, 2023
New CSHL research on Rett syndrome could also have implications for autism spectrum disorders, dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease.
The evolution of autism research
May 25, 2023
The conversation around autism has evolved over the past two decades. So has CSHL research. This retrospective shows how we’ve helped move the needle.
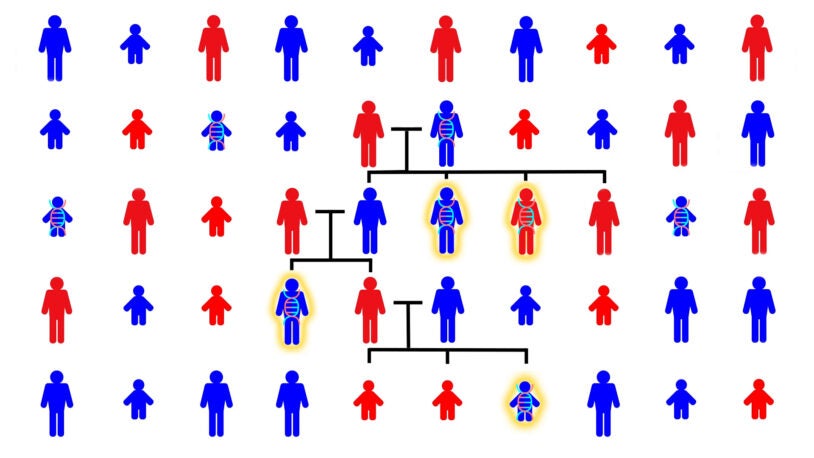
Autism in the family tree
May 23, 2023
CSHL scientists have studied the genetics of autism across hundreds of family trees. This animated video shows what they’ve found.
Siblings with autism share more of dad’s genome, not mom’s
May 22, 2023
CSHL study of more than 6,000 volunteer families overturns a long-held assumption about the genetic origins of autism spectrum disorder.
A bridge to the future of autism research
May 18, 2023
With access to premier technology and expertise, CSHL primes early-career scientists for breakthrough studies of autism spectrum disorder.
Lucas Cheadle named HHMI Freeman Hrabowski Scholar
May 9, 2023
Cheadle was selected for his leadership in neuroscience research and advancing diversity, equity, and inclusion in science.
How well do you know autism spectrum disorders?
April 24, 2023
April is National Autism Awareness Month. Test your knowledge of autism spectrum disorders with this short quiz.
The science of supermoms
January 10, 2023
Moms know best, but how do they learn it? A new study offers insights into the mental reward system that nurtures maternal instinct.