Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) have discovered a new function of the body’s most important tumor-suppressing protein.
Cold Spring Harbor, NY — Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) have discovered a new function of the body’s most important tumor-suppressing protein. Called p53, this protein has been called “the guardian of the genome.” It normally comes to the fore when healthy cells sense damage to their DNA caused by stress, such as exposure to toxic chemicals or intense exposure to the sun’s UV rays. If the damage is severe, p53 can cause a cell to commit preprogrammed cell-death, or apoptosis. Mutant versions of p53 that no longer perform this vital function, on the other hand, are enablers of many different cancers.
Cancer researcher Dr. Raffaella Sordella, a CSHL Associate Professor, and colleagues, today report in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences the discovery of a p53 cousin they call p53Ψ (the Greek letter “psi”). It is a previously unknown variant of the p53 protein, generated by the same gene, called TP53 in humans, that gives rise to other forms of p53.
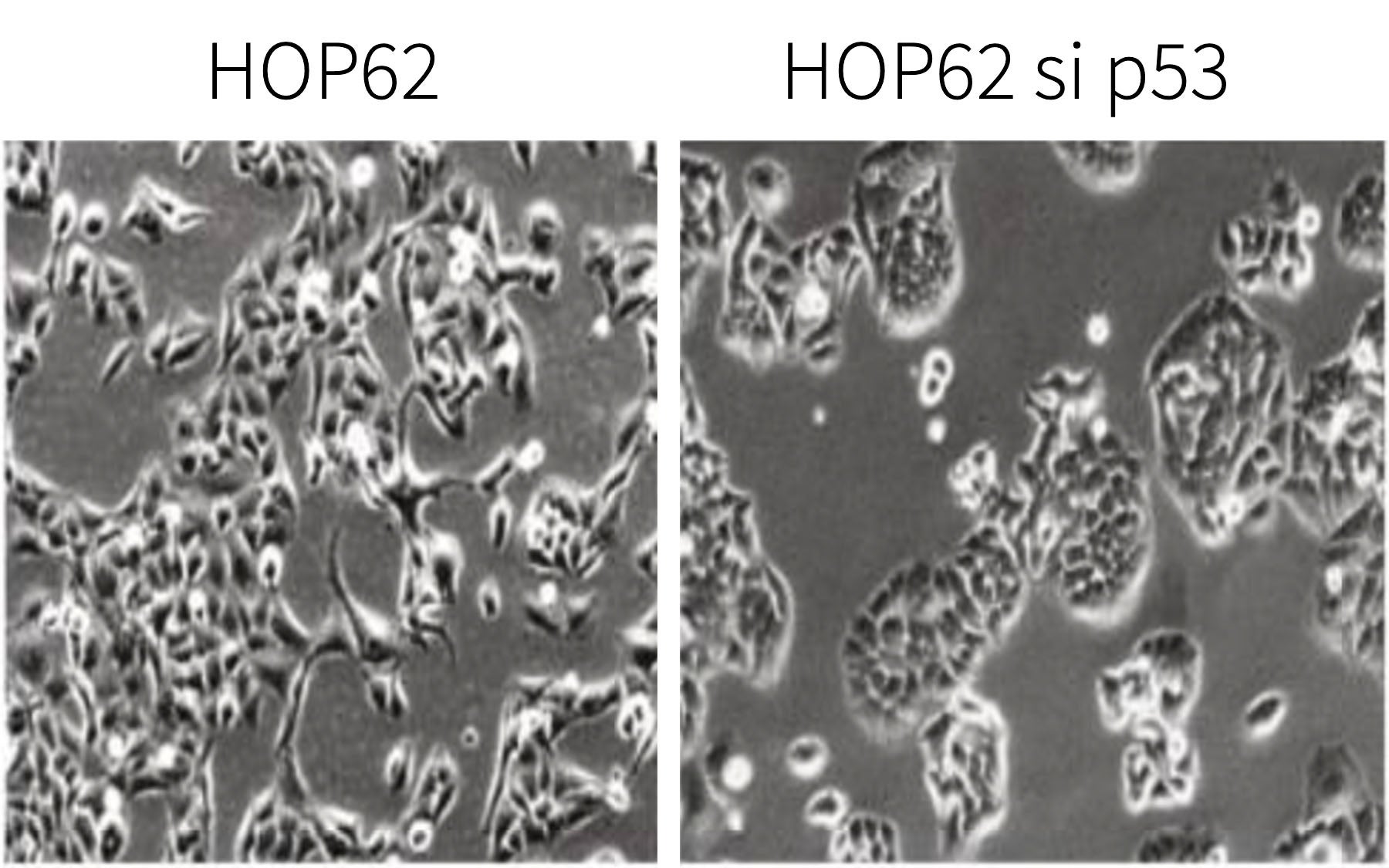
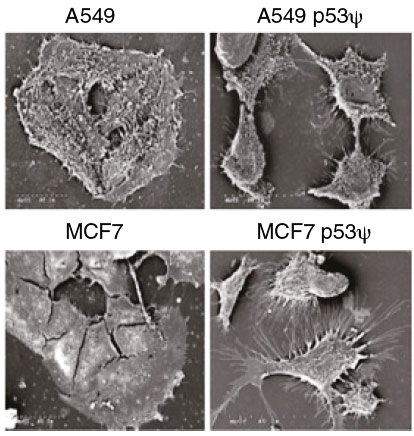
Sordella and colleagues observed that p53Ψ, when expressed, reduces the expression of a molecular glue called E-cadherin, which normally keeps cells in contact within epithelial tissue, the tissue that forms the lining of the lung and many other body organs. This is accompanied by expression of key cellular markers associated with tumor invasiveness and metastatic potential. (These are markers of EMT, or epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.) Consistently, Sordella and her team found levels of p53Ψ to be elevated in early-stage lung tumors with poor prognosis.
Careful investigation revealed that p53Ψ generates pro-growth effects by interacting with a protein called cyclophillin D (CypD), at the membrane of the cell’s energy factories, the mitochondria, and by spurring the generation of oxidizing molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS).
p53Ψ was found by the team to be inherently expressed in tumors but also in injured tissue. “This is intriguing,” Sordella says, “because generation of cells bearing characteristics of those seen in wound healing has been seen previously, in tumors.”
It is possible, Sordella says, that more familiar p53 mutants associated with tumor growth and metastasis may have “hijacked” those abilities from the program used by p53Ψ to promote healing during tissue injury. A cellular program, in other words, that evolved over eons to heal may have been hijacked by mutant p53 to enable cancers to spread out of control.
The team is currently investigating p53Ψ in wound healing to help clarify its role. Confirmation would lend support to the theory that mutant p53 hijacks that function to help advance pro-metastatic processes in cancer.
Written by: Peter Tarr, Senior Science Writer | publicaffairs@cshl.edu | 516-367-8455
Funding
The research discussed in this release was funded by a grant from the Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation.
Citation
“p53Ψ is a transcriptionally inactive p53 isoform able to reprogram cells toward a metastatic-like state” appears online ahead of print the week of July 28, 2014 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The authors are: Serif Senturk, Zhan Yao, Matthew Camiolo, Brendon Stiles, Trushar Rathod, Alice M. Walsh, Alice Nemajerova, Matthew J. Lazzara, Nasser K. Altorki, Adrian Krainer, Ute M. Moll, Scott W. Lowe, Luca Cartegni and Raffaella Sordella. The paper can be obtained at: http://www.pnas.org/content/early/recent