Cold Spring Harbor, NY — As a brain grows, the neurons within it establish themselves, forming lasting connections with their neighbors. They’re creating the vast cell networks that ensure a mind and body run smoothly. Now, researchers have determined how a crucial kind of neuron called a chandelier cell (ChC) forms connections with other neurons, opening new avenues for understanding mental illness.
Chandelier cells “are beautiful structurally, and are restricted to mammals,” Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professor Linda Van Aelst explains. “That’s very unique.”
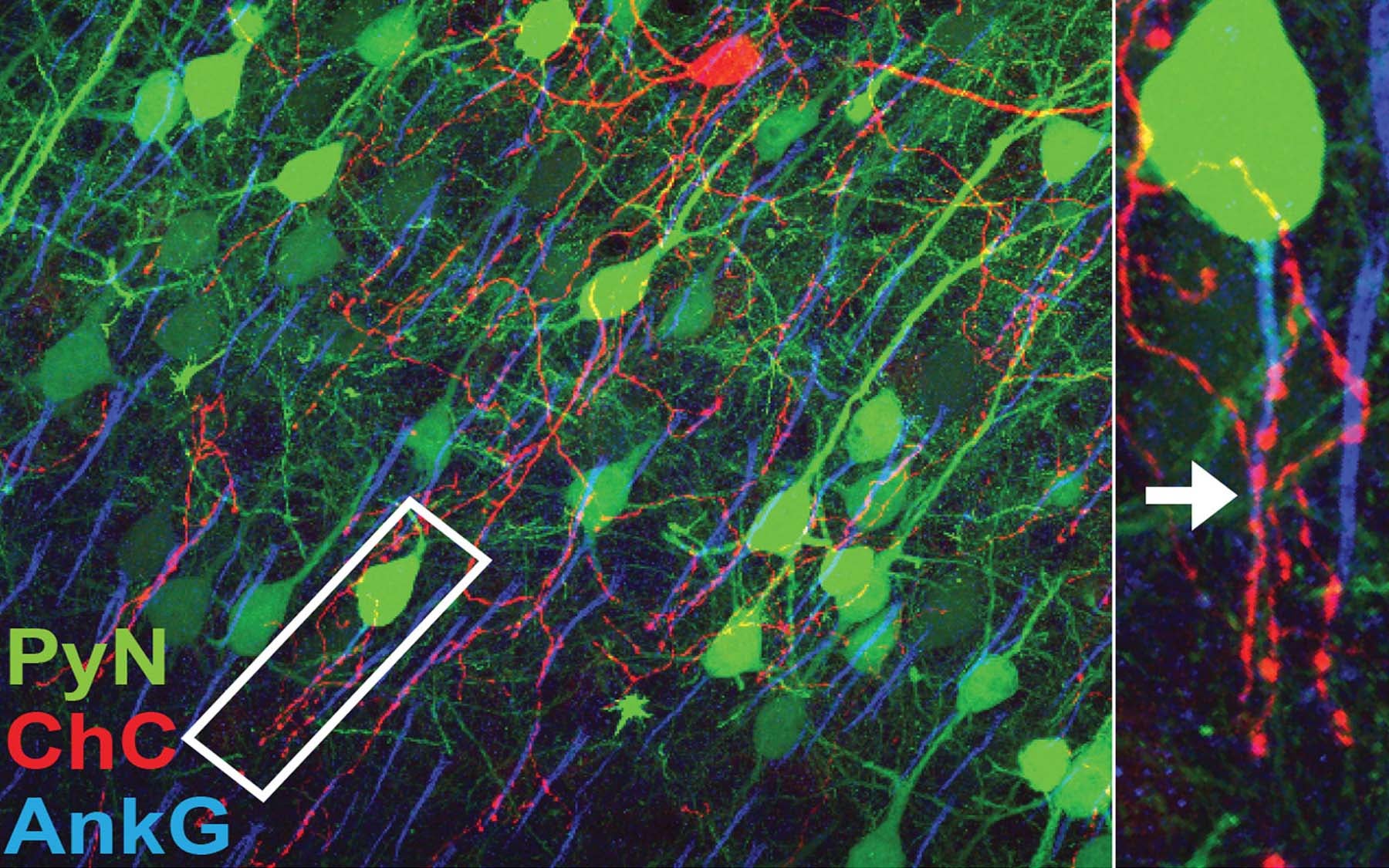
Compared with other kinds of neurons in the mammalian brain, these cells are sparse in number. But they make up for lower density by reaching far with long, drooping fibers that make them look like their namesake. It’s the endings of these reaching fibers, called cartridges, that allow ChCs to connect with many neighboring excitatory pyramidal neurons (PyNs). ChCs connect with PyNs at one particular anatomical location, the axon initial segment—a spot where a spiking PyN generates its transmittable message.
So how does the ChC make lasting connections? That’s what Van Aelst and researchers Nicholas Gallo and Yilin Tai set out to discover. They learned that the presence of one specific molecule was the key in determining whether a ChC’s arbor would connect with any PyN. They published their findings in the latest issue of Neuron.
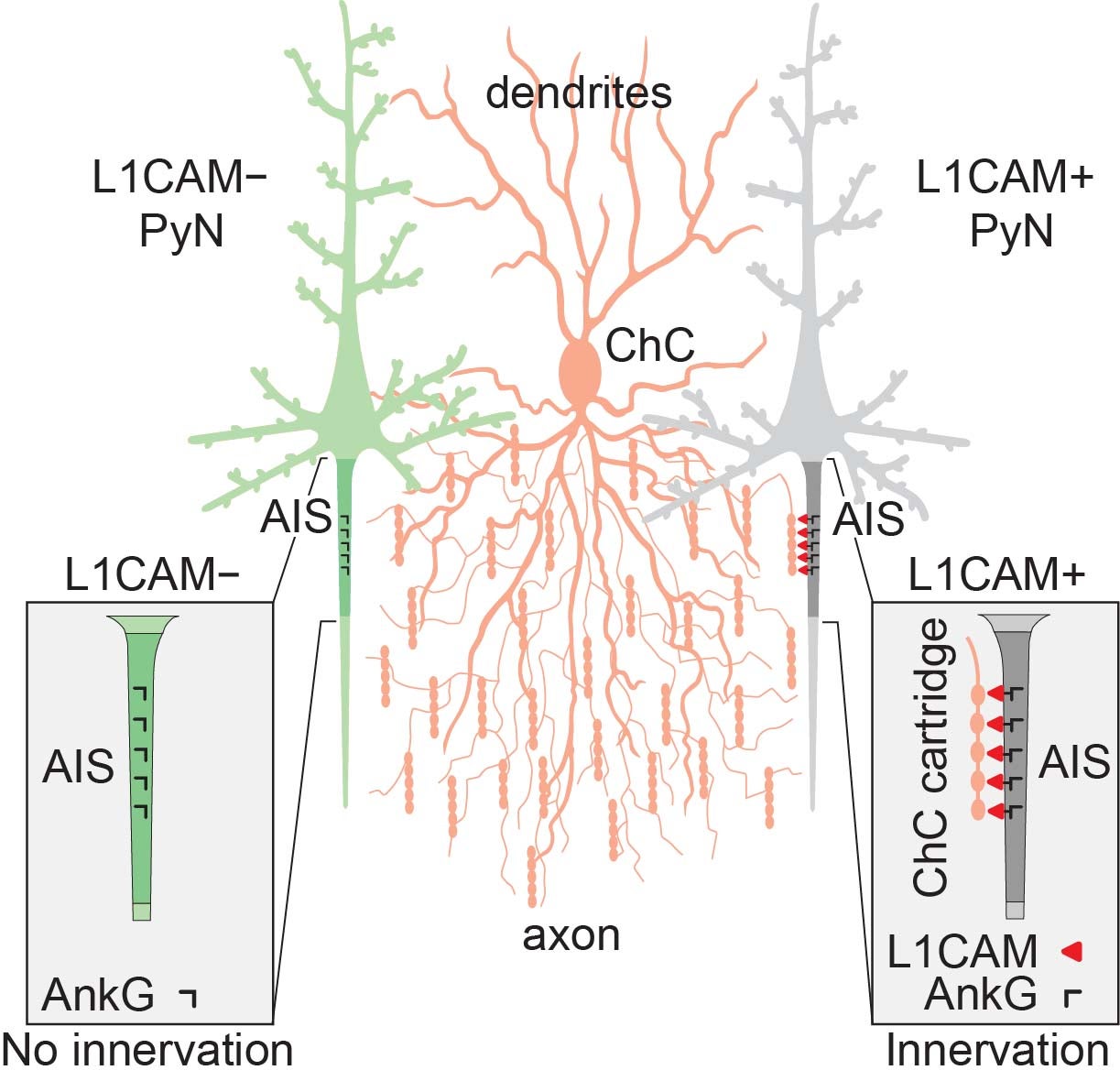
“Imagine these connections as something like Velcro. On one cell you have little hooks. On the other, you have felt. They latch together,” Gallo says. “In our situation, we found this molecule called L1CAM is the ‘hooks.’”
L1CAM can be found on the surface of PyNs, where “it latches onto the ChC cartridge, forming synapses. This is the first molecule that has been shown to regulate this,” Gallo says.
Gallo, Tai, and Van Aelst tested 14 molecules that might mediate the ChC-to-PyN connection, but only L1CAM seemed to be essential. Without it, a PyN is ignored by a ChC during “establishment,” or the initial forming of a connection. Further, the molecule is required not just for the initial connection, but for maintaining established connections.
“If you get rid of L1CAM after all synapses have been formed, you still see an impact on the contact point,” says Van Aelst. “It falls apart.”
Poor connectivity of ChCs has been linked to neurological conditions like schizophrenia and epilepsy. Now, the researchers hope to identify the “felt” side of this molecular Velcro, potentially leading to new avenues for neurological drug discovery.
Written by: Brian Stallard, Content Developer/Communicator | publicaffairs@cshl.edu | 516-367-8455
Funding
This research was funded by the National Institutes of Health and a NARSAD Young Investigator grant.
Citation
Tai, Y. et al, “Axo-axonic Innervation of Neocortical Pyramidal Neurons by GABAergic Chandelier Cells Requires AnkyrinG-associated L1CAM” in Neuron on March 4, 2019.
Principal Investigator

Linda Van Aelst
Professor
Harold and Florence & Ethel McNeill Professor of Cancer Research
Cancer Center Program Co-Leader
Ph.D., Catholic University of Leuven, 1991