When a stem cell commits to becoming a leaf cell, how does a polycomb gene-repressing protein complex know where in the genome to go, and when?
Cold Spring Harbor, NY — The normal development of an animal or plant can be compared in at least two ways with the successful performance of a great symphony. The whole is the product of a great number of events involving contributions by many different “players”; and these contributions must occur in a precise and almost perfectly coordinated temporal and spatial sequence.
In simple animals like the fruit fly and more recently in plants and mammals, scientists have been able to identify some of the principal players in the developmental symphony. Today, a team of researchers from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) explains for the first time the operation of a mechanism in plants that controls a class of key developmental regulatory genes, called homeobox genes.
The homeobox genes under study, called BREVIPEDICELLUS (BP) and KNAT2, need to be active in plant stem cells in order for the cells to maintain their non-specialized character. Stem cells are totipotent: they can develop, or “differentiate,” into any plant cell type, depending on signals they receive which send them down the developmental path. When the moment is just right for plant organs such as leaves to begin to grow, BP and KNAT2 are switched off so that development can proceed.
“We were already familiar with the players in this regulatory mechanism, which have been conserved, or preserved, by evolution across species from flies to plants to animals,” says CSHL Professor Marja Timmermans, who led the research team. “What we have not understood until now is how, in plants, the action of the players is very precisely coordinated in time and space.”
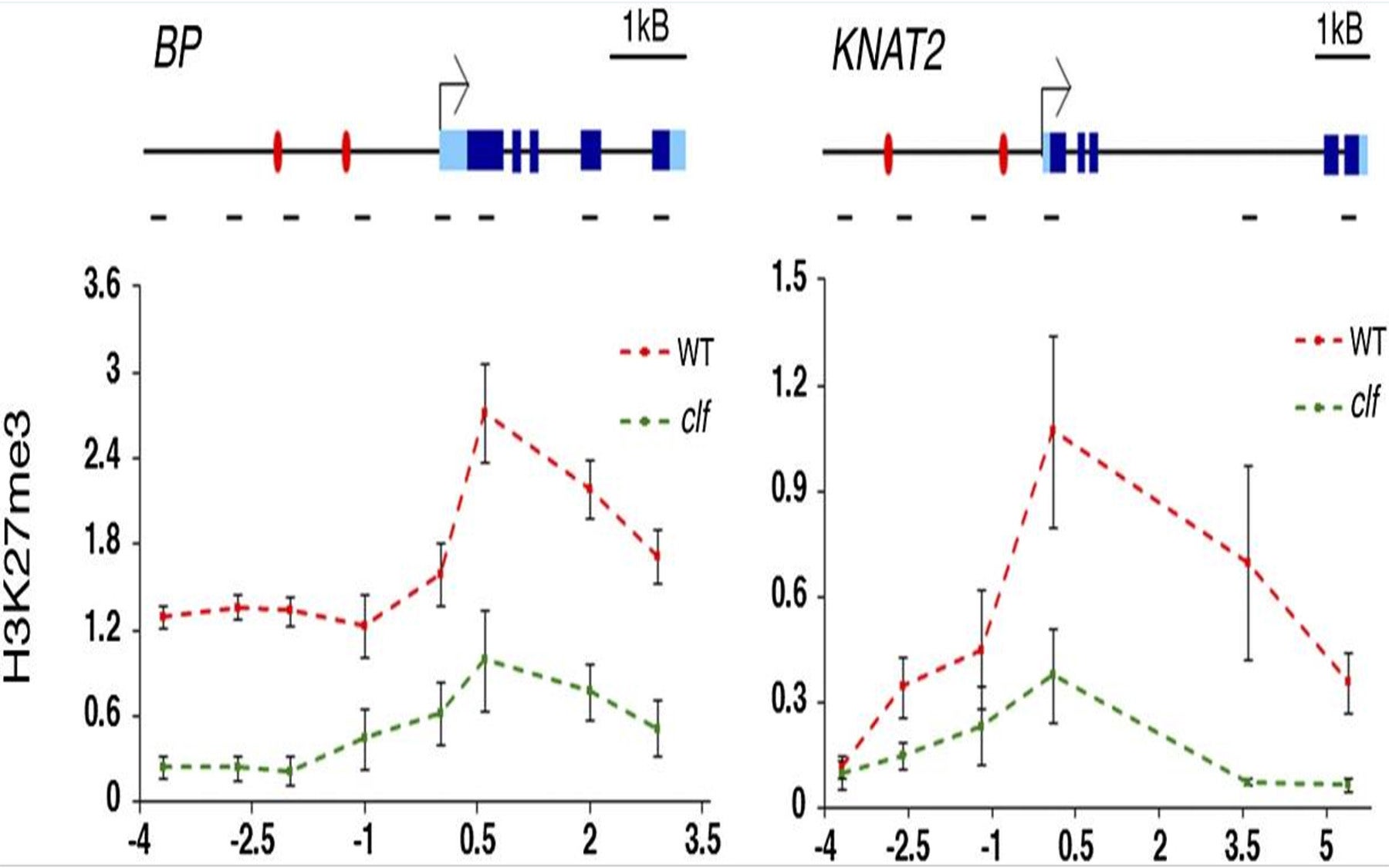
It turns out that a highly conserved assembly of polycomb proteins, called Polycomb-repressive complex2 (PRC2), spurs a process called epigenetic regulation that physically marks targeted genes—in this case, BP and KNAT2—for repression. But how do these protein complexes know where along the plant cell’s genome to go, and when, in order to induce this gene-repressing effect?
The key discovery by the Timmermans team, which appears online today in the journal Genes & Development, is the identification of the mechanism that brings PRC2 to specific sites along the genome precisely in those cells committed to become a leaf.
Timmermans’ team showed that PRC2 physically interacts with DNA binding proteins that attach to plant DNA in specific genome regions just ahead of where the homeobox genes are situated. In the plant they studied, Arabidopsis, those DNA binding proteins are ASYMMETRIC LEAVES1 (AS1) and AS2. When a stem cell commits to becoming a leaf cell, AS1 and AS2 become active, attach at the DNA sites near BP and KNAT2, and recruit PRC2 to repress these homeobox genes. The epigenetic mark made by PRC2, which acts like a cellular memory, is heritable, and is essential in order for leaves and other plant organs to develop.
In other locations along the genome, other analogous mechanisms are surely at work, says Timmermans, whose broad interest in this research concerns its implications for patterning in development.
Timmermans is intrigued to learn the effects of tweaking with the timing of regulatory gene expression and repression. She suspects small adjustments to expression of master regulators during development are one of the means by which evolution proceeds over vast stretches of time.
She also notes that by tweaking these developmental regulatory systems, it might be possible to beneficially affect plant regeneration—the process in which a new plant is generated from the leaf of an existing one. This process involves de-differentiating a mature cell and returning it to a primitive developmental state before once again allowing it to proceed down a developmental path—a process akin to that employed in the making of human IPS (induced pluripotent stem) cells.
Written by: Peter Tarr, Senior Science Writer | publicaffairs@cshl.edu | 516-367-8455
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the New York State Department of Health (C024308) and the National Science Foundation (MCB-0616114).
Citation
“The ASYMMETRIC LEAVES complex maintains repression of KNOX homeobox genes via direct recruitment of Polycomb-repressive complex2” appears online March 6, 2013 in Genes & Development. The authors are: Mukesh Lodha, Cristina F. Marco and Marja C.P. Timmermans. The paper can be viewed online at: http://genesdev.cshlp.org/content/early/recent